
Efficacy studies
Learn more about the treatment of ADHD in children, adolescents and adults.
Treatment of ADHD in Children
Significant improvement in attention and behaviour with sustained beneficial effects has been shown in children versus placebo||
- In the two placebo-controlled crossover studies (Studies 1 and 2), symptoms of ADHD were evaluated by laboratory school teachers using the SKAMP (Swanson, Kotkin, Agler, M-Flynn, and Pelham) laboratory school rating scale
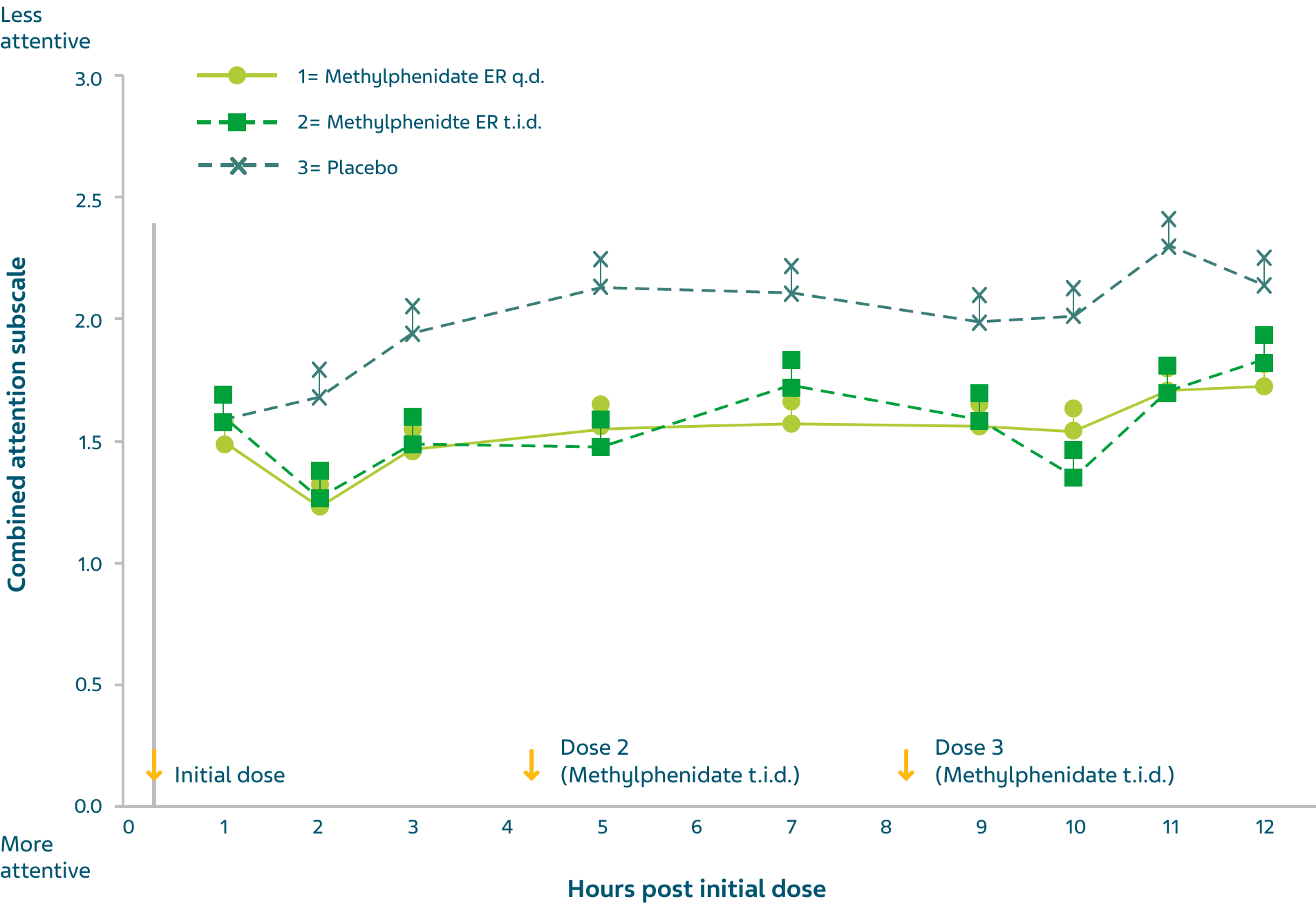
- Significant improvement in attention and behaviour versus placebo was shown consistently across the two studies (p <0.005)
- Efficacy was maintained through 12 hours after dosing
- Sustained beneficial effects of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets q.d. therapy seen throughout the laboratory classroom day were comparable in duration to those with methylphenidate hydrochloride t.i.d.
Adapted from the ACT-Methylphenidate ER Product Monograph
Mean laboratory school teacher SKAMP Ratings of Combined Attention (Study 1) with methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets q.d. (18, 36, or 54 mg), methylphenidate hydrochloride t.i.d. over 12 hours (15, 30, or 45 mg total daily dose), and placebo. Error bars represent mean plus standard error of the mean. The sample sizes for methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets, methylphenidate hydrochloride t.i.d., and placebo groups were 60, 62, and 60, respectively.
q.d. = once a day; t.i.d. = three times a day
||Three double-blind, active- and placebo-controlled studies were conducted in 416 children aged six to twelve. The controlled studies compared methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets q.d. (18, 36, or 54 mg), methylphenidate hydrochloride t.i.d. over 12 hours (15, 30, or 45 mg total daily dose), and placebo in two single-centre, 3-week, crossover studies (Study 1 and Study 2), and in a multicentre, 4-week, parallel-group comparison (Study 3). The primary comparison of interest in all three trials was methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets versus placebo.
Treatment of ADHD in Adolescents
Demonstrated to be effective in the treatment of ADHD and generally well-tolerated in adolescents at doses up to 72 mg/day (1.4 mg/kg/day)¶
In a randomized, double-blind, multicentre, placebo-controlled trial (Study 4) involving 177 patients, methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets were demonstrated to be:
- Effective in the treatment of ADHD
- Mean scores for the investigator rating on the ADHD Rating Scale for methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets were significantly improved relative to placebo (CON –14.93; PLA –9.58; p=0.001)
- Mean scores for methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets and placebo, respectively, at the end of the double-blind phase were 16.62 and 21.40, compared to 31.55 and 30.99 at baseline
- Generally well tolerated in adolescents aged 13 to 18 at doses up to 72 mg/day (1.4 mg/kg/day)
¶Of 220 patients who entered an open 4-week titration phase, 177 adolescent patients aged 13 to 18 who met the DSM-IV criteria for ADHD were titrated to an individualized dose (maximum 72 mg/day) based on meeting specific improvement criteria on the ADHD Rating Scale and the Global Assessment of Effectiveness with acceptable tolerability. Patients who met these criteria were then randomized to receive either their individualized dose of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets (18 – 72 mg/day, n = 87) or placebo (n = 90) during a 2-week double-blind phase.
Treatment of ADHD in Adults
Demonstrated statistically significant superiority in improving the investigator-rated Connors’ Adult ADHD Rating Scale (CAARS) total scores compared to placebo△
In a 5-week randomized, double-blind, multicentre, placebo-controlled, dose-response trial (Study 5) involving 401 adults aged 18 to 65 years who met the DSM-IV criteria for ADHD:
- All doses of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets (18 mg, 36 mg, and 72 mg/day) were statistically significantly superior to placebo in improving the CAARS total scores at double-blind endpoint compared to baseline (mean change of -7.6 for placebo, -10.6 (p=0.0146) for methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets 18 mg, -11.5 (p=0.0131) for methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets 36 mg, and -13.7 (p<0.0001) for the methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets 72 mg
- Statistically significant differences compared to placebo were first observed at Week 1
△5-week, randomized, double-blind, multicentre, placebo-controlled, dose-response trial (Study 5) was conducted in 401 adults with ADHD aged 18 to 65 years using once daily methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets fixed doses of 18 mg, 36 mg, and 72 mg. Efficacy was evaluated by the mean change from baseline to double-blind endpoint in the investigator-rated Connors’ Adult ADHD Rating Scale (CAARS) total score.
Refer to the Product Monograph for indications, contraindications, warnings, precautions, drug interactions, and dosing.
Download Product MonographLearn more about ACT Methylphenidate ER



